Okay, so this point you might, you might be convinced on NFTs, you might just be keeping an open mind. Either way, thank you for coming this far. And now let’s dive into another question. Why are NFTs possible only today after the advent of blockchain technology? why have we never been able to have things that are scarce, that are ownable on the internet before? And ultimately that comes down to the nature of the blockchain and why the blockchain is so foundationally revolutionary for NFTs and more? So ultimately, what is the blockchain? Well, in a very simple sense, you can think of the blockchain as a distributed ledger of the source. In the very beginning, the ledger was made just to keep track of financial transactions, and that was when bitcoin was invented. That was the first-ever use case of watching technology. So history lesson, in 2008 Satoshi Nakamoto, and that’s a pseudonym. No one really knows who he is. Invents bitcoins, which is the first-ever use case of blockchain technology. In fact, the blockchain was invented specifically to create bitcoin, which Satoshi Nakamoto was trying to model as a sort of digital gold. And so his goal was to create the first-ever digital currency that could be trustless that someone could trust in the same way that we trust gold in the real world without having to trust in government like the U.S. government to back the U.S. dollar or the European union to euro or the Great Britain crown to be backed by Great Britain, gold is one of the few currencies in the real world where you don’t have to trust a government to manage fiscal policy well, to not over inflate, to print a huge amount of this currency, and then you know, dilute the supply and the value over time. Gold is something that retains its value extremely well because no one can create more of it.
It just comes out of the ground. And there was created billions of years ago. To date, we have never figured out a way to create more gold. And so because of that, you can trust that gold will always be scarce and because gold will always be scarce, we can trust, maintain, and hold its value well over time. That is true. Gold has retained its value for thousands of years, whereas no fiat currency, meaning a currency backed and created by a government, has ever been able to maintain its value over even a thousand years or even a couple of hundred years. And so because of that fact, the ability to create digital gold is quite valuable, because gold is quite cumbersome. There’s a reason we don’t use it for transactions because no one goes to the car dealership and you shave off an ounce of gold, you give it to pay for your car or you go to buy coffee, and you shave off a little like a slice of gold to do that. That would be pretty crazy. This is why people usually use fiat currencies. Despite all the downsides. Despite the fact that you have to trust this fiat currency will retain its value. So if you could create a digital gold, that would be powerful. You can check Here.
But how could you possibly do it in a way where you can trust that no one’s just going to be able to create more of this currency over time? Well, that’s where the blockchain comes in, and that is the same innovation that enables NFTs today, to also be trustless for us to also be able to believe that no one can ever just create a new certificate saying that there is the owner of this art piece online or the other digital asset. So how does that work? Well, it’s fascinating.
How was blockchain used for bitcoin?
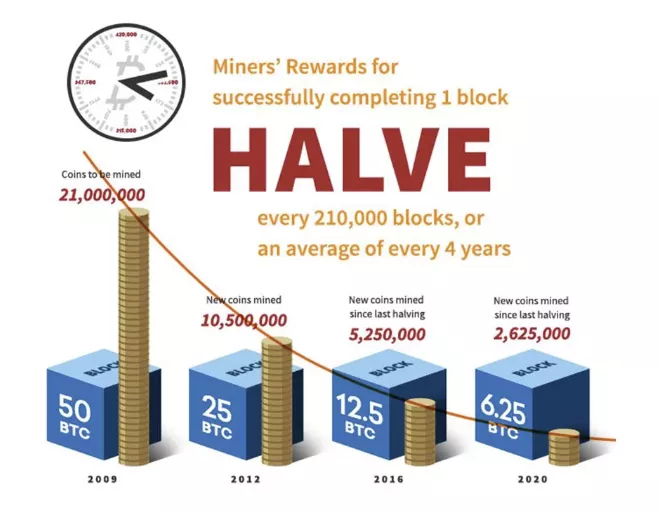
Let’s talk about how the blockchain was used in the case of bitcoin, and then we can translate that into how it’s used for NFTs today. So in the case of bitcoin, the goal is to create an asset that could replicate gold but digital. And by that, we mean something that could be permanently guaranteed to be scarce. And so there is a guarantee that there will only ever be 21 million bitcoins ever created. And in fact, we know exactly the carefully regulated supply of bitcoin over time that will be produced.
At the very beginning of time in 2008, there were 50 bitcoins are created on average every ten minutes, and then four years later in 2012, about halved to 25 bitcoins every ten minutes. Then again, in 2016, that halved again to just be 12.5 bitcoin. And today in 2020, we had the last halving, which made bitcoin issuance just 6.125 bitcoin every ten minutes, on average. That is going to continue going down until essentially, there is no more bitcoin left to be produced every ten minutes or so. And when that happens, we know precisely in about 2040, there’ll only ever be a complete supply of about 21 million bitcoins. And so because of that, we can trust that bitcoins will retain their value just like gold because there is no infinite supply that can ever be created out of thin air.
So how is blockchain-enabled at? First a little backup. Let’s talk about why scarcity is even valuable because it’s the same actually for bitcoin and NFTs. And if you have only 21 million bitcoin, let’s just think in a perfectly ideal economic world, let’s say you’re valuing the economic pie. Maybe you’ve heard of that concept before.
And let’s say there are like a hundred bushels of corn. That’s the only thing that ever exists in the world. And you have a 100 bitcoin that values 100 bushels of corn. So one bitcoin equals one bushel of corn. Now, let’s say you doubled as supply now you have 200 bitcoins and you only still have one hundred bushels of corn. Well, if you’re doing, then two bitcoin now must equal one-bushel corn. Because you don’t have more corn. That 100 bushels of corn are now worth 200 bitcoin, so each corn is now worth just half of what it used to be before, one bitcoin now only buys half a bushel of corn. And so now we can see in this very simplistic model if the economic pie stays at the same. The amount of value in the world stays the same, which is not true in the real world. You know, the world grows. We produce more value over time. But just for this, this example, let’s pretend they’re only ever 100 bushels of the corn. That’s all that will ever exist. If you create more money, that is going to dilute every individual unit of money that represents this entire economy. So that ultimately is why having scarcity in your money supply is valuable. It’s kind of the same thing with art. If you think about why photographers and other artists often just do limited edition prints. They say, Hey, I promise I’m only ever going to make 100 photos of this, negative that I created, or I’m only ever going to make 100 prints of this piece that I created. That’s the same reason because they realize, if there are unlimited versions of this in the world, then people aren’t going to value it in the same way, Because they say, Oh, I can just create a new one for ten bucks. Why do I need to pay $10,000 for one of just 100 limited edition prints? And so we can see, kind of this works in the same way. Scarcity is extremely important for both fungible currencies like bitcoin or the U.S. dollar, and also non-fungible items like art.
Okay. So now that we know that, let’s talk about how the blockchain enables us to have this guaranteed belief that there are only ever be a scarce 21 million bitcoin in the world in the next post “How does the Blockchain guarantee us a scarcity of tokens?”